What are BRC 20 Tokens?

The evolution of blockchain and cryptocurrencies brings us new concepts that transform our perception of digital assets. Examples abound in this regard, but one of the most recent is BRC-20 tokens.
The hype for the token has swept across the crypto world with the BRC-20 standard, which has just surfaced; the unique offer of creating fungible tokens on the Bitcoin blockchain assuredly would be a game-changer.
In this article, we will examine what BRC-20 tokens are, how they function, their potential, and how they differ from other token standards like ERC-20 on Ethereum.
What are BRC-20 Tokens?
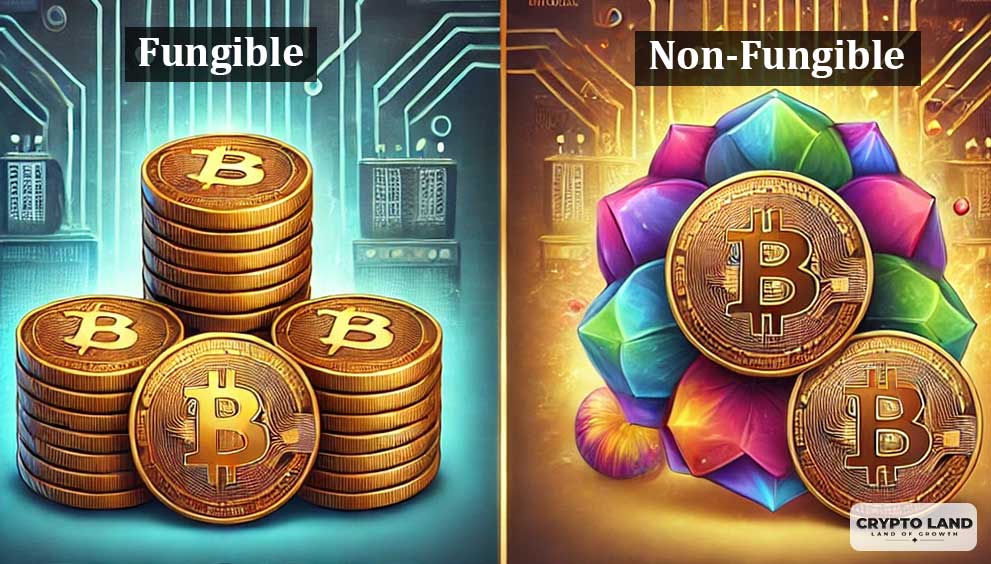
BRC-20 tokens are a class of fungible tokens existing on the Bitcoin blockchain Ordinals Protocol lays the possibility for this.
Unlike Bitcoin, which was originally conceptualized as a decentralized digital currency and not a token-creating platform, this BRC-20 narrative becomes the opposite scenario. It makes it possible for developers to create and trade fungible tokens on Bitcoin’s base layer.
An anonymous developer referred to as Domo proposed the BRC-20 standard in March 2023 as an experiment inspired by a very widely-used Ethereum token standard called ERC-20. It tried to bring those capabilities, that exist on blockchains like Ethereum, to Bitcoin but in a more limited fashion.
However, it is essential to note that BRC-20 tokens are still in an experimental phase, and their adoption is not as rich and scalable in features as compared to the ERC-20 tokens on Ethereum, which boasts the support of smart contracts.
How do BRC-20 Tokens Work?
To get a proper understanding of BRC-20 tokens, it’s first important to get a conceptual understanding of the core mechanism they work with Ordinals Protocol.
An ordinals protocol can quite basically be thought of as allowing any satoshi, which is the smallest unit of bitcoin, to be “inscribed” with metadata; in other words, attaching extra information onto them.
This information can be images and text as well, but, as is the case with BRC-20 tokens, it is fungible token data.
When intending to create a BRC-20 token, the user will need to generate an ordinal inscription, which defines the token’s properties.
Properties will include name, maximum supply, and all other necessary parameters that might define such a token. From that point onward, the token may be transmitted or received through Bitcoin transactions-basically, just like we move Bitcoin from one wallet to another.
Unlike Ethereum’s smart contracts, which automate the issuance, transfer, and burning of tokens, BRC-20 relies purely on inscriptions tied to satoshis.
This makes it far more manual and non-programmable compared to Ethereum, with automatic transfers of tokens via smart contracts.
Another of the key limitations of BRC-20 tokens is that they cannot interact with dApps or leverage the level of functionality that one can do with ERC-20 tokens.
Key Features of BRC-20 Tokens
Ordinals Inscriptions. From the above information, it was learned that BRC-20 tokens are made possible by ordinal inscriptions. This inscription enables people to attach metadata to satoshis through which fungible tokens can be minted.
Minting and Transfer: The mint process of a BRC-20 is relatively quite simple but much less automated than on other blockchains. Users can then mint tokens by executing one of the special mint transactions created for it specifying the name, amount, and even setting a supply cap. Such minted tokens can then be transferred between wallets with the usage of standard Bitcoin transactions.
Manual Interaction: One feature of BRC-20 tokens is that there is no involved complicated programming. In contrast, although smart contracts govern transactions as well as token logic in ERC-20 tokens, BRC-20 tokens require direct interaction with the Bitcoin protocol by a user to create and transfer tokens.
The Pros and Cons of BRC-20 Tokens
While BRC-20 tokens represent an exciting new direction for Bitcoin, they are not without challenges and limitations. Let’s break it down with both the pros and cons of this token standard.
Pros
Leveraging Bitcoin’s Security: One of the greatest benefits of BRC-20 tokens is that they inherit the strong security model of Bitcoin. Bitcoin is, in fact, the most secure blockchain in the world because of its massive mining power and its decentralized nature.
Future for Innovation: As the standard of BRC-20 matures, it will likely engender entirely new types of applications in DeFi and DEXs along with token economies making use of the proven security of Bitcoin and its global network.
Cons
No Smart Contracts: The BRC-20 tokens natively do not support complex operations like token swaps, lending, borrowing, or staking in comparison to ERC-20 tokens. Unlike Ethereum and all other smart contract platforms, BRC20 tokens do not natively support automated token swaps, lending, borrowing, or staking.
Manual Processes: Since BRC-20 tokens are to be minted and transferred with ordinal inscriptions, which is a manual process, they are missing all the automation and programmability that other token standards were able to support. This would hugely hinder the adoption process, especially for more advanced applications.
Scalability Problems: Bitcoin’s network is secure but wasn’t built with high-throughput transaction use cases in mind, like Ethereum or Solana. It’s somewhat difficult to scale BTC 20 token transactions using Bitcoin due to the small block size of the network and hence slow transaction times.
Experimental Nature: It is more important to note that tokens on BRC-20 are still purely experimental. The concept is very new, and it is unknown how the Bitcoin community would take it in as well as scaling its potential issues.
BRC-20 and ERC-20 Tokens Comparison
Another key comparison would be between the BRC-20 standard and its Ethereum counterpart-ERC-20 standard. Here are several key distinctions:
Blockchain Base: BRC-20 tokens operate on the Bitcoin blockchain, and ERC-20 tokens work on the Ethereum blockchain. Bitcoin is more focused on security and decentralization, but Ethereum has the characteristics of programmability from the smart contract nature.
Smart Contracts: The next difference is that ERC-20 tokens have a smart contract powering the tokens and, hence, can perform complex actions automatically. The simple ordinal inscriptions of BRC-20 tokens, however, do not depend on smart contracts.
Transaction Costs and Speed: Ethereum transactions are faster, but they cost more because the network has high gas fees. Bitcoin’s transactions are slower and cheaper, yet if the BRC-20 tokens take off, the Bitcoin network is probably going to get congested.
The Future of BRC-20 Tokens
Beyond its original design as a digital currency, the BRC-20 standard may offer a new direction in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
With solutions like the Lightning Network BRC-20 tokens may well become a heavy player in the crypto landscape.
Put simply, BRC-20 tokens unlock the possibility of creating fungible assets on the Bitcoin blockchain-tapping into its security but only within the strictures of smart contract functionality, which it lacks.
⚠️ Disclaimer:
Crypto Land is an impartial marketing and educational platform, not a financial advice service. Therefore any content provided, hosted, or expressed by Crypto Land does not constitute financial advice or recommendation, and as such Crypto Land will not be liable for any losses incurred during trading or investing.



















![Top Altcoins in October [2024] You Should Look Out For 20 Top Altcoins in October [2024] You Should Look Out For](https://cryptolandoff.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Top-Altcoins-in-October-2024-You-Should-Look-Out-For.jpeg)