Key Insights
- Multiple exchanges have been hacked so far, over the last decade.
- Many of these have collapsed because of the breaches, including Mt Gox and Cryptopia.
- On the other hand, many exchanges have survived with a combination of strategies including 1:1 asset backing, prompt communication, insurance policies and more.
- Some great examples include BitFinex and ByBit, which was recently hacked for $1.5 billion.
The crypto industry is thrilling, mostly because of how unpredictable it can be.
Prices tend to skyrocket and crash, fortunes are made and lost, and the most impenetrable platforms get breached with billions of dollars stolen.
One of the most devastating blows a crypto exchange can face is the issue of hacks.
When crypto hacks happen, a lot of crypto is stolen, which can be a huge disaster.
However, the main issue is what comes after—liquidity crises. An inability of a crypto exchange to settle transactions, due to the unavailability of funds.
How do exchanges respond to such crises, and what lessons are there to be learned from past failures?
Let’s jump right in.
Understanding Liquidity Crises in Crypto
A liquidity crisis for a crypto exchange, can be very similar to a bank run—except that this example of a bank run is on steroids.
When an exchange is hacked and the news gets out, investor trust evaporates instantly.
A rush almost always happens with investors, panicking as they attempt to withdraw their funds before the “lose everything”.
Such a large amount of demand puts even more pressure on the freshly hacked exchange, creating more of a problem as it struggles to satisfy customers, while assessing the damage of the hack.
Exchanges typically have to sell off some of its reserve assets at unfavorable prices to meet the withdrawal demand.
Sometimes, the pressure hits critical levels, and the exchange simply freezes withdrawals entirely.
This creates a very dangerous cycle that has ruined many exchanges, and left many investors penniless.
Lessons from Crypto’s Biggest Liquidity Crises
Hacks are not a new concept in the crypto space. This means that there are many real-world examples to draw from.
Here are some of the most infamous cases in crypto history:
Mt. Gox (2014)
Mt Gox was one of the biggest crypto exchanges in the world at some point. Bitcoin was relatively young at the time of the hack—barely five years old—and Mt Gox controlled around 70% of all BTC transactions at its peak.
However, in 2014, the exchange suffered a massive hack, in which a staggering 850,000 BTC—worth billions today was stolen.
This created one of the worst liquidity crises in crypto history, and caused the total collapse of the exchange.
Mt. Gox simply lacked the security measures it needed to protect its assets, and had no transparent accounting system in place.
When the hack happened, there was no contingency plan, and the exchange was left unable to cover its losses.
It declared bankruptcy, and is now known as one of the worst failures in crypto history.
Bitfinex
The BitFinex was the next major crypto hack, and happened around two years after the Mt Gox incident.
The BitFinex exchange was hacked for around $72 million worth of Bitcoin—which again, is worth billions today.
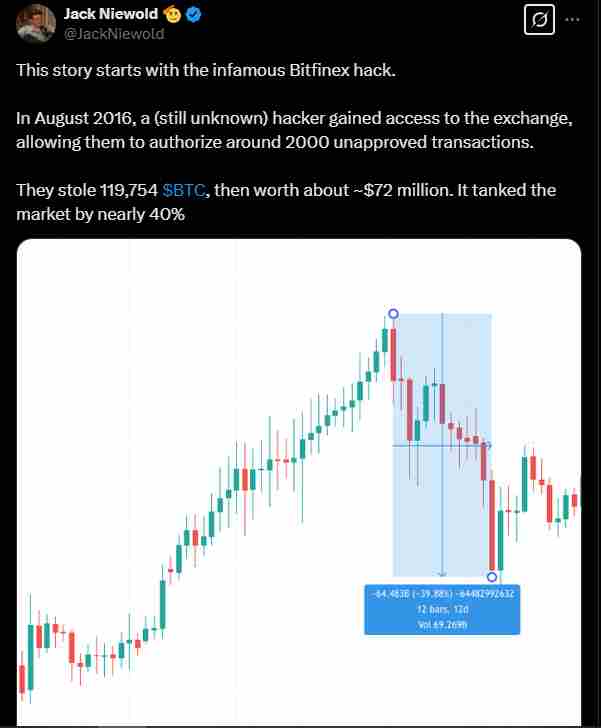
However instead of shutting down and declaring bankruptcy like Mt Gox did, BitFinex did something interesting: it socialized the losses.
It offered its affected users $BFX tokens, which represented a debt owed by the exchange.
Over time, BitFinex was able to buy back these tokens from its users, repaying them in full.
While the decision to distribute the losses among its users was highly controversial at the time, the strategy worked and BitFinex was able to recover.
Cryptopia
Cryptopia, based in New Zealand was hacked three years after BitFinex in 2019. However, Cryptopia ended up like Mt Gox and was unable to recover like BitFinex did.
The Cryptopia aftermath was one of the messiest crypto exchange crashes in history, as liquidators struggled to return remaining assets to users.
FTX
The FTX crash is likely one of the most well known exchange failures till date. This hack likely played a major role in the start of the 2022 bear market.
Prior to being hacked, the exchange, led by its CEO and founder Sam Bankman-Fried misused customer funds between FTX and its sister firm, Alameda Research.
The exchange reported a hack in November of 2022, suspected to be up to $477 million.

This hack played a huge part in revealing the extent of FTX’s customer fund mismanagement.
It also led to a scramble among customers to withdraw their funds, only to discover that the funds were never there to begin with.
Bankman-Fried was arrested shortly after, and is currently serving a 25-year prison sentence.
ByBit
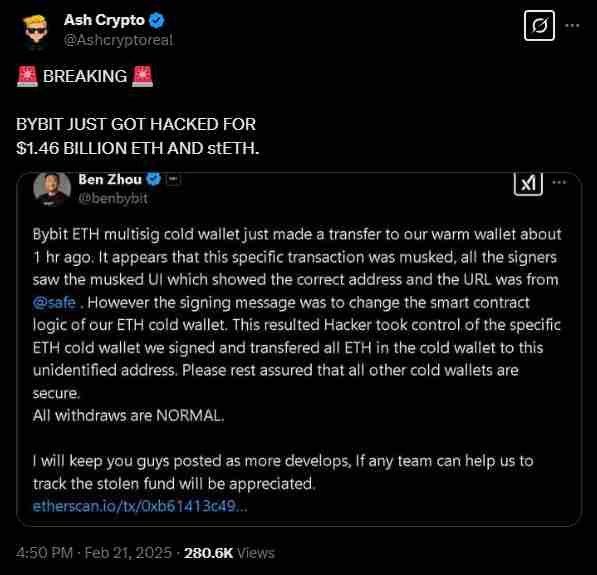
Bybit was the latest major exchange to be hacked.
Hackers, believed to be related to the North Korean Lazarus Group recently hit the exchange with an exploit, and made away with a staggering $1.5 billion worth of ETH.
The breach itself is now known as the largest crypto exchange theft in history.
However despite the scale of the hack, Bybit was transparent with its customers and offered them regular updates.
The exchange also reassured users that their funds were safe and backed 1:1.
The exchange even partnered with blockchain analytics firms and successfully froze a certain portion of the funds.
ByBit remains afloat even at the time of writing, with one of the most well-handled breaches of this size.
How Crypto Exchanges Survive Liquidity Crises
Exchanges that withstand crises often start with a combination of security and transparency with their customers. Some of the ways that this has happened include:
1. Maintaining Reserve Funds and Insurance
Exchanges often set aside reserve funds, or get insurance policies to cover their losses. These safety nets also help to reassure customers that their funds are safe, even during emergencies.
2. Cold Storage and Security Measures
Exchanges often minimize risks by keeping the majority of their assets in cold storage. These wallets are offline, and are therefore out of the reach of hackers.
Some exchanges even apply multi-signature wallets and regular audits to improve their protection.
3. Transparent Communication
During crises, exchanges are often open and honest about the extent of the damage with their users.
Exchanges that keep their customers informed, often experience less panic and are less likely to suffer a ‘bank run”.
4. Partnering with Liquidity Providers
Exchanges like Binance and many others often partner with liquidity providers and market makers.
These entities make sure that there are always buy and sell orders available, which can be useful for reducing the effects of liquidity squeezes.
5. Developing Contingency Plans
A well prepared exchange should have a crisis management plan in place, including protocols for handling security breaches and liquidity shortages.
Overall, the crypto market is still evolving, and so are its challenges.
History has shown that when liquidity crises hit, the exchanges that make it (and even rebuild) are the ones with the best contingency plans in place.







