Fungible vs. Non-Fungible: A Brief Comparison of Crypto-Assets
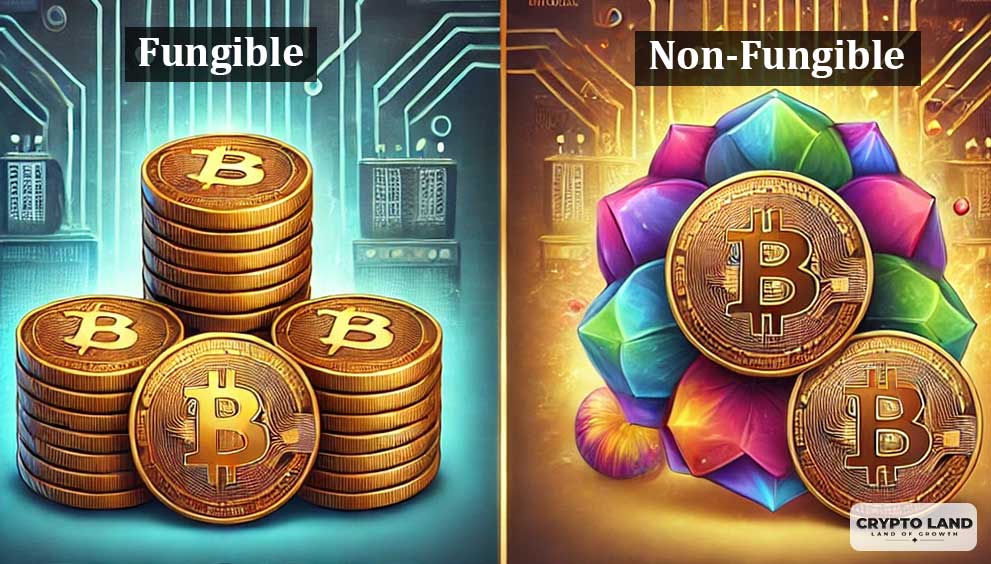

What Are Fungible Tokens?
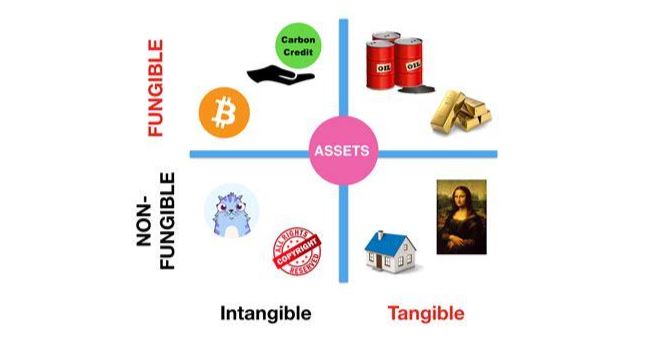
Fungible and Non-fungible tokens are used to refer to two different types of tokens. Fungible tokens are identical to each other and can be divided into smaller numbers, similar to a currency, while non-fungible tokens are unique in all matters.
Let’s dive deeper into fungibility and non-fungibility, see how they work, their applications and why the difference matters so much.
What Does Fungibility Mean?
Fungibility is the characteristic of an asset in which each unit is equal and substitutable with another. Meaning, that a fungible asset is something that can be traded on a one-to-one basis because all units have the same value and characteristics.
For example, two $10 bills are and will always be equivalent in value and represent equal purchasing powers for equal goods and services. Thus, dollars are fungible.
Most of the cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) in cryptocurrency are fungible by that definition.
What Does Non-Fungible Mean?
Non-fungibility, obviously is opposite to fungible and means that every asset has a uniqueness and cannot be exchanged with each other. A non-fungible token has distinguishing features that make it unique in comparison with others, though they appear to be alike to a great extent.
For example, valuable artwork such as “Everyday: The First 5000 Days” by Beeple.
Each of them is unique and represents an asset that cannot be exchanged with another.
Non-Fungible Tokens or NFTs represent assets that do not meet the fungibility criteria. Each of them is unique even if two NFTs are a part of the same collection.
Differences Between Fungible and Non-Fungible Tokens
1. Interchangeability
Fungible Tokens: Each fungible token is interchanged with another. An example is swapping where USDT on Solana blockchain can be swapped for USDC on Polygon because both are USDC tokens.
Non-Fungible Tokens: Each token is unique and cannot be replaced by another. For example, if you have a BAYC NFT, you can’t just replace it by any other NFT, say MAYC or CryptoPunk. They wouldn’t have the same value or properties or even look.
2. Divisibility
Fungible Tokens: Fungible assets can be divided into small quantities. You can cut one Bitcoin into smaller fragments such as 0.5 BTC or 0.0001 BTC. This makes it easier to do flexible transactions.
Non-Fungible Tokens: NFTs are not divisible into fragments. It is not possible to have a fraction of any given NFT; one can own the asset fully. This characteristic of indivisibility defines non-fungible tokens.
3. Standardization
Fungible Tokens: As fungible assets are the same, standardisation can easily occur. Every Bitcoin transaction, for example is standardized as all of its dealings and directives are on an equal level, making exchange easier and much manageable across different platforms.
Non-Fungible Tokens: The value of NFTs is extremely unique and based on its specific attributes. An NFT of the same sports moment or the same collectible within the same collection has different features and scarcity, which make its value different.
4. Value Determination
Fungible Tokens: Only the value of fungible tokens is based on supply and demand in the market. All tokens of the same type (example: Bitcoin) have the same market value.
NFTs: Most of the times, value of NFTs is subjective, and thus depends on issues such as the token’s ability to be rare, or even the reputation of the creator, how historical it is, and the demand that collectors have for it. This explains why sometimes one NFT can be sold in millions, while another has little or no value.
Appreciation of Fungible and Non-Fungible Tokens
Usage of Fungible Tokens in Crypto
Fungible tokens take up the majority of the cryptocurrency world. Some of them include:
Bitcoin, Ethereum, BNB, Solana, Dogecoin, XRP, Stablecoins (USDT, USDC) and many others
NFTs in Crypto
NFTs have become mainstream recently and unlock new possibilities for digital ownership and creativity. Here are some common applications:
Art NFTs have revolutionized the way art existed. Now artists can create tokens of their work and sell it on exchanges like OpenSea, Blur or Rarible. Every piece of artwork created with NFTs is unique, and one can buy, sell, or trade it on different platforms.
Gaming and Utility NFTs can be used to represent in-game items and characters, so players can 100% own these assets and even kind of take them for themselves. Examples are games like Axie Infinity and Decentraland. Players can even trade, sell, or show off their digital assets to peers.
Metaverse NFTs make it possible to own virtual real estate in blockchain-based worlds like The Sandbox and Decentraland.
Why the Fungible/Non-fungible Difference Matter?
Fungible tokens are perfect for financial applications and form the core of DeFi systems. Their interchangeability and divisibility make them ideal applications for payments, lending, staking, and liquidity pools.
Non-fungible tokens, however, are about ownership and uniqueness. They really come handy in presenting digital art, rare items, intellectual property, and nearly everything in which uniqueness features greatly. NFTs enable new forms of communication between creators and consumers in ways never possible before. Digital goods now have new markets through NFTs.
Conclusion
In summary, fungible and non-fungible tokens serve highly dissimilar purposes in the blockchain ecosystem.
For instance, fungible tokens are usually used when referring to a kind that can be interchanged, often being used as forms of money or things that can be exchanged at equal value. These attributes definitely define NFTs as unique digital assets, each holding its own individual value based on the rarity or distinctive characteristics making them impossible to be interchanged.
Well, fungible tokens are particularly better for transactions and equal exchanges but not so much for representing ownership or uniqueness in the digital world. As is the case with other roles, interchangeability and the type of value held is the primary difference between the two varieties.



















![Top Altcoins in October [2024] You Should Look Out For 20 Top Altcoins in October [2024] You Should Look Out For](https://cryptolandoff.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Top-Altcoins-in-October-2024-You-Should-Look-Out-For.jpeg)