What are dApps?

Decentralized Applications, or dApps, are apps that exist on the blockchain and rely on its infrastructure to execute their functions. Being decentralized eliminates the risk of traditional apps, such as over centralization, failure, high downtime, server crashes, and other issues.
These Decentralized Applications do not have any single location, control, or management. They are typically based on the blockchain and offer uninterrupted access to the end user.
Further, as these apps do not have any control, most are run democratically. One example is the ENS, or Ethereum Name Service, which lets you customize your blockchain addresses.
What is DApp technology?
dApps are based on blockchains and operate using their virtual machines. For example, a dApp like 1inch, a DEX aggregator, relies on an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
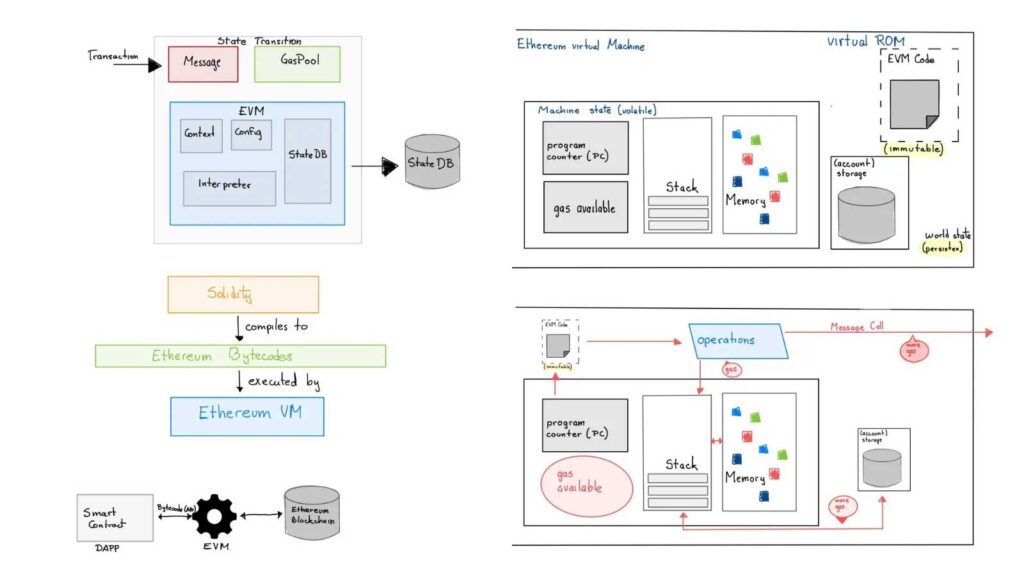
A blockchain virtual machine like EVM handles all the computations and operations of the Ethereum blockchain. It pulls resources from different Ethereum nodes and uses the aggregated computing power to execute operations like dApps, transactions, mint NFTs, etc.
dApps use these virtual machines and pay them through transaction fees, referred to as gas fees.
dApps usually generate a lot of transactions and, therefore, need a scaling solution to keep the costs down. This is because Layer-1 chains like Ethereum often charge higher fees. Earlier, before the Dencun Upgrade, these dApps used to rely on Layer-2 chains like Arbitrum or Polygon or high throughput chains like Solana.
Benefits of dApps
Privacy
dApps often use a non-invasive way and do not ask for any personal data. They support user anonymity. Further, any data generated through most dApps does not carry personal information.
For example, DeFi dApps like Uniswap allow all users to perform actions like lending, borrowing, swapping crypto, etc., without asking for identity information. This is the opposite of banks, which typically have a long KYC process.
No Single Point of Failure
Since dApps run on a blockchain-based virtual machine like an EVM, they do not have a single point of failure. An EVM comprises several geographically distributed nodes. If any single node goes offline, others can easily take over its operations.
For example, after the CrowdStrike crash, all the Windows computers would not have crashed if they had followed the distributed architecture of dApps.
Lack of Censorship
Unlike centralized apps like Facebook, where a single authority can direct its operations at will, many dApps do not have a single point of control. Even if someone censors or stops one node from operating, hundreds of others can replace it in a few minutes.
dApps vs. Web Apps vs. Mobile Apps
dApps differ from web apps and mobile apps in terms of architecture and operations. We have explained them below in brief.
A web app is software that uses cloud computing to offer different solutions to its users. One such web app is the Zoho billing software, which helps you create bills for your business. These apps rely on a single server and have a centralized control, i.e., the company that publishes them. Another example is the Microsoft 365. These are different from websites which only provide static data and do not perform heavy operations.
On the other hand, there are mobile apps, which are applications that run on your mobile and use the internet to send or receive information. They give you some control over their usage but are largely governed by the publisher that creates them. Some examples include Facebook, Snapchat, Uber, Amazon, PayPal, etc.
However, in the case of dApps, the full control rests with the user. Open-source dApps can be copied, modified, and often re-sold with your own branding. Further, these dApps do not have any single point of origin as developers from diverse backgrounds create and publish them via team effort. Lastly, dApps do not rely on any single server and are run by DAOs, which govern its operations.
Top Ethereum-based dApps
Ethereum is the most popular blockchain for running dApps because of its highest grade of security and resilience. The blockchain hosts over 400 dapps.
Other blockchains that support dApps are Solana and the BNB Chain.
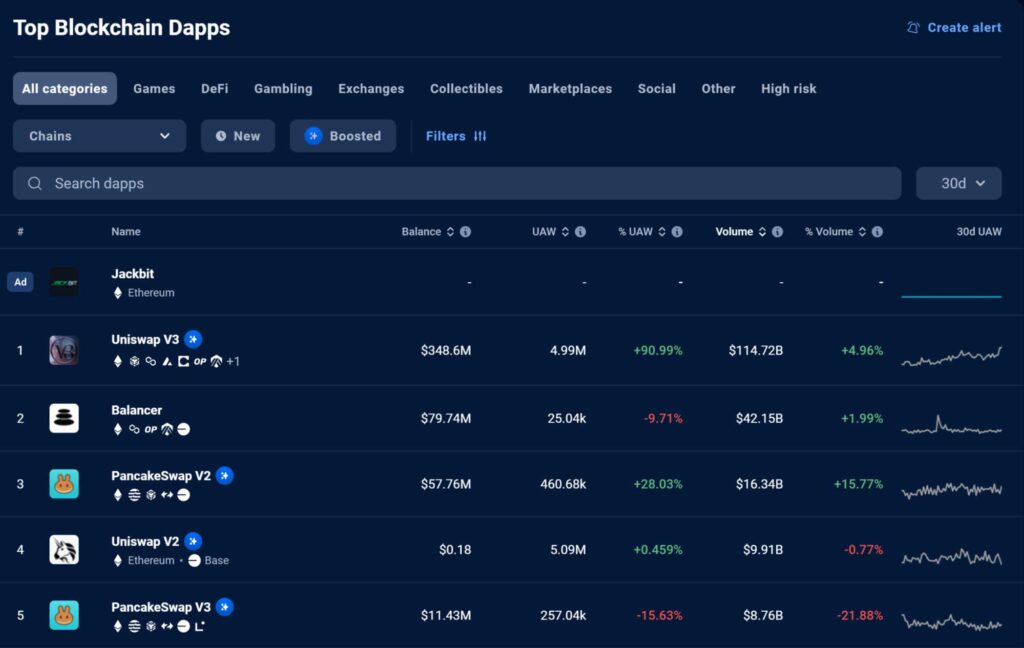
Top 5 Dapps Listed on Dappradar
Uniswap
Uniswap is a defi protocol that lets you perform financial operations like lending crypto, borrowing crypto, depositing it to earn money, swapping assets, sending them to other users, or even selling them for stablecoins. Uniswap exists as a Layer-3 application (dApp) on the Ethereum blockchain.
Ethereum Naming Service
Ethereum Naming Service or ENS is a dApp that allows you to create shortened versions of your blockchain address to send or receive ETH easily. The dApp charges a few dollars, often less than 10, to provide a multi-year registration. ENS is a dApp built on the Ethereum blockchain.
Opensea
Opensea is an NFT marketplace that exists as a dApp and lets users buy and sell NFTs. It also allows you to create your own NFTs for free. The dApp is one of the top popular NFT marketplaces on Web3 and is built on the Ethereum blockchain.

Crypto Land is an impartial marketing and educational platform, not a financial advice service. Therefore any content provided, hosted, or expressed by Crypto Land does not constitute financial advice or recommendation, and as such Crypto Land will not be liable for any losses incurred during trading or investing.



















![Top Altcoins in October [2024] You Should Look Out For 20 Top Altcoins in October [2024] You Should Look Out For](https://cryptolandoff.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Top-Altcoins-in-October-2024-You-Should-Look-Out-For.jpeg)